Full disk encryption
IoT data is sensitive
Industrial internet of things (IIoT) devices store sensitive data, configuration files, log files, authentication secrets and software intellectual property. Any compromise to the integrity of data stored on devices can have damaging consequences.
If bad actors gain physical access to a device, they can extract user data. To prevent such scenarios, cryptography is needed to protect data confidentiality.
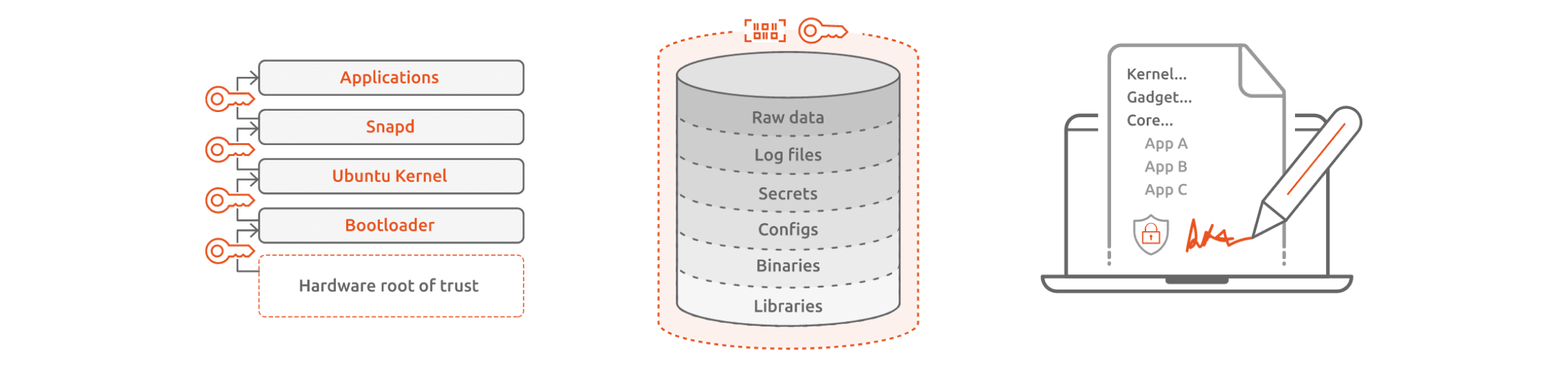
Secure data at rest
Data security and integrity can be achieved by storing the secrets in secure elements or Trusted Platform Modules (TPM), or by using specialised software-enabled stores that use symmetric key encryption.
The most reliable technique is to cryptographically ensure data integrity by using digital signatures. Private key based cryptographic signatures can attest to the actual data at the time of signing. The integrity of signed data can be validated, ensuring the integrity prior to applying software and firmware updates.
The same applies to validating configuration and log files. The signing operation is usually performed in a hardware trust root, such as a TPM, where the signing key can also be securely stored.
Full disk encryption on Ubuntu Core
ARM and x86
Ubuntu Core abstracts the root of trust implementation for full disk encryption. As a consequence, Ubuntu Core full disk encryption can be enabled for both ARM and x86 SoCs.
Free for pre-certified boards
Full disk encryption is available out of the box on certified devices, with TPM support, at no additional cost. An enablement fee is required to fully certify Ubuntu Core on non-certified boards.
How it works
Digital signatures
Ubuntu Core uses digital signatures to cryptographically ensure data integrity. Private key based cryptographic signatures can attest to the actual data at the time of signing. At any point in the workflow, the integrity of signed data can be validated, thereby ensuring the integrity prior to applying software and firmware updates.

Root of trust
Data at Rest integrity can be achieved by securely storing the private key used for encryption in hardware/TPM, or by using specialised software-enabled stores which employ symmetric key encryption. Using this key sensitive endpoint data stored on the disk can be protected.

Secure your devices
Get in touch with a Ubuntu security expert to discuss the advanced security requirements of your application.
